Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Introduction to AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer the stuff of science fiction. This rapidly evolving field has woven itself into the fabric of our lives, from the smartphones in our pockets to the self-driving cars on the horizon. But what exactly is AI? In essence, it's the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence, including learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. This doesn't mean robots replacing humans (yet!), but rather machines using sophisticated algorithms and data to perform tasks once thought exclusive to the human mind. From healthcare to finance, AI is transforming industries, offering exciting possibilities while also raising important questions about ethics, bias, and the future of humanity. Whether you're curious about the technical details or simply want to understand how AI will impact your life, this journey into the world of artificial intelligence is just the beginning.
Types of AI
- Reactive Machines:Think of these as the simplest form of AI, akin to pre-programmed robots. They operate based on pre-defined rules and respond directly to their environment. Consider Deep Blue, the chess-playing AI, which analyzed the board and chose the best move based on its vast library of pre-programmed strategies. However, these machines lack the ability to learn or adapt beyond their initial programming.
- Limited Memory AI:As the name suggests, these AI systems can store and access past experiences to inform their current actions. Imagine a self-driving car equipped with this technology. It would not only react to immediate obstacles but also remember the layout of previous routes, improving its navigation over time. This learning is limited to specific tasks and doesn't translate to entirely new situations.
- Theory of Mind AI:This hypothetical type of AI aims to understand and respond to the emotions and intentions of others. Imagine a virtual assistant that not only answers your questions but also senses your frustration and adjusts its communication style accordingly. While still in its early stages of development, this type of AI could revolutionize human-computer interaction by fostering deeper connections and understanding.
Applications of AI
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):NLP encompasses a range of techniques that teach computers to understand and manipulate human language. This involves breaking down language into its building blocks like words, phrases, and sentences, and then analyzing their meaning, structure, and intent. Through algorithms and statistical models, NLP systems learn to recognize patterns and extract meaning from language data, performing tasks like:
* Machine translation: Transforming text from one language to another while preserving its meaning and nuance.
* Text summarization: Condensing large amounts of text into concise summaries, capturing key points and information.
* Speech recognition: Converting spoken language into text with increasing accuracy and understanding natural human speech patterns.
* Chatbots: Creating conversational AI agents that can interact with humans in a natural and engaging way.
* Machine writing: Generating text content like articles, poems, or scripts based on specific instructions or styles.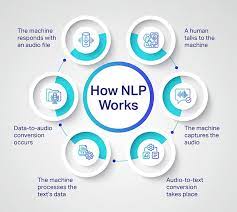
- Computer Vision:At its core, CV aims to give machines the ability to "see" and understand the visual world as humans do. This involves analyzing digital images and videos, identifying objects, their properties, and relationships within the scene. Unlike simple pattern recognition, CV strives for deeper understanding, enabling machines to:
* Classify objects: Distinguish between different objects (e.g., a cat, a car, a person) within an image.
* Detect objects: Locate specific objects within an image or video, even if partially obscured.
* Recognize scenes: Understand the broader context of an image, identifying the environment or activity depicted.
* Track objects: Monitor the movement of objects across consecutive video frames.
* Segment images: Divide an image into meaningful regions based on color, texture, or other visual cues. - Robotics:Robotics, the science and engineering of designing, building, operating, and using robots, has transcended the realm of science fiction and firmly planted itself in our reality. From industrial assembly lines to surgical assistants, robots are transforming industries, pushing the boundaries of technology, and raising intriguing questions about the future of humanity. Let's explore the fascinating world of robotics, unpacking its history, applications, and potential impact.
Challenges in AI
- Lack of Ethical Guidelines
- Data Privacy Concerns
- Job Displacement
